Global mortality rates are declining, but are rising among young people in some regions
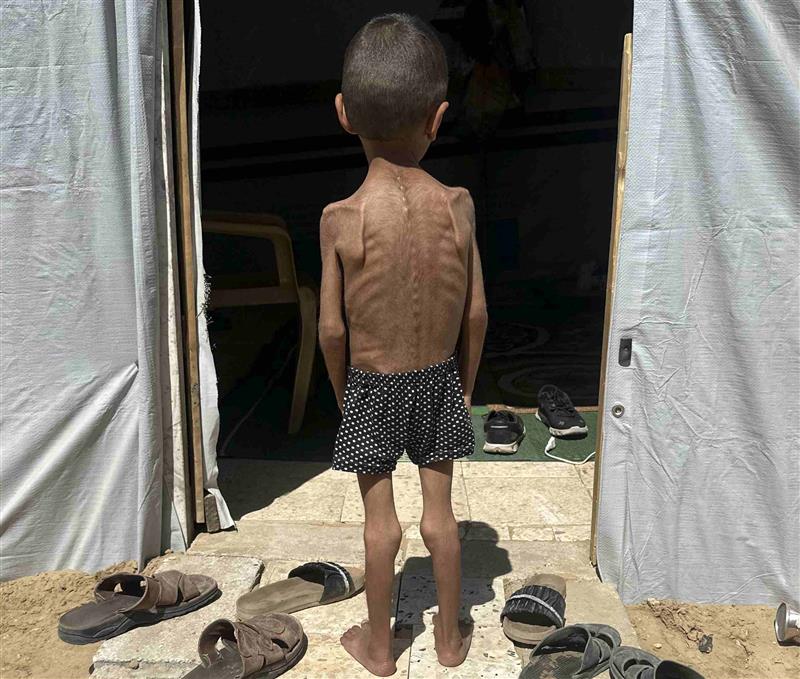
According to the Global Burden of Disease study, and despite deep inequalities between countries, global life expectancy in 2023 was more than 20 years higher than in 1950. However, deaths among young people increased in some regions such as North America, Latin America—due mainly to suicide and drug use—and sub-Saharan Africa—mainly due to infectious diseases and injuries. Researchers also estimate that almost half of all deaths and disabilities could be prevented by modifying some of the main risk factors. The results are published in The Lancet and will be presented at the World Health Summit, being held in Berlin, Germany, from October 12 to 14.