
Complutense University of Madrid
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Lecturer of Palaeontology at the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM) and affiliated researcher at CENIEH
Professor of Prehistory and member of the Institute for Feminist Research at the Complutense University of Madrid
Associate Professor at Camilo José Cela University, researcher at the HM Hospitales Health Research Institute (Madrid) and collaborating researcher in the Department of Personality, Evaluation and Clinical Psychology at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Astrophysics and Director of the Space Astronomy Group at the Complutense University of Madrid
Acute Cardiac Care Unit Coordinator. Cardiovascular Institute. Hospital Clínico San Carlos. Madrid; Associate Professor of Medicine at Complutense University of Madrid; and President of the Association of Ischemic Heart Disease and Acute Cardiac Care of the Spanish Society of Cardiology
Accredited professor, lecturer at the Faculty of Psychology and director of the Research Group on Testimony Psychology at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Biochemistry at the Complutense University of Madrid, president of the Spanish Society of Dietetics and Food Sciences (SEDCA) and treasurer of the Spanish Federation of Nutrition, Food and Dietetics Societies (FESNAD).
Lecturer in the Department of Theoretical Physics and member of the Dynamics of Disordered Systems group at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Animal Health at the Complutense University of Madrid and advisor to the WHO in the field of antibiotic resistance
Permanent professor at the TRANSOC Institute of the Complutense University of Madrid

Migratory birds are particularly affected by the climatic, ecological and urban changes resulting from the constantly changing world in which we live. Their survival is at risk, as are the ecosystems in which they live. We analyse the threats they face on a cyclical basis during their migratory routes and why it is important to protect them.

A survey conducted in the United States by the Harvard Opinion Research Program shows that more than four in ten American adults (44%) say that changes in federal leadership will cause them to lose confidence in the recommendations of public health agencies, compared to 28% who say they will trust them more. The survey, which included a sample of more than 3,300 participants aged 18 and older, also revealed that other health issues have strong support among Democrats and Republicans, such as chronic disease prevention, pandemic protection, and reducing maternal and infant mortality.

An American team has developed a ‘smart’ computer keyboard that could be used for the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. The prototype is a flexible device, linked to a mobile application, whose keys detect slight variations in the pressure applied by the user, allowing for the quantitative analysis of motor symptoms. The study, published in Science Advances, presents the validation of the keyboard with three people with Parkinson's.

A fragment of a human face discovered in 2022 at the Sima del Elefante site in the Sierra de Atapuerca (Burgos) and dated to between 1.1 and 1.4 million years ago represents the oldest known face in Western Europe. The fossil, nicknamed ‘Pink’, does not belong to Homo antecessor, but has been provisionally catalogued as Homo affinis erectus. The find, which is published in the journal Nature, could indicate that Western Europe was populated by at least two species of hominids during the Early Pleistocene: Homo affinis erectus and, later, Homo antecessor.

In 2050 there will be 25.2 million people with Parkinson's disease worldwide, which represents an increase of 112% from 2021, largely due to the ageing of the population, according to a modelling study published by The BMJ. The number of people living with this disease – prevalence across all ages – per 100,000 inhabitants is expected to increase by 76% – and by 55% when age differences are corrected.

A study led by researchers in Canada has analysed the relationship between perimenopausal symptoms and later cognitive and behavioural problems in nearly 900 women. Their findings are that those with more symptoms were more at risk of cognitive problems and dementia later in life. The results are published in the journal Plos One.

The 16th meeting of the United Nations Conference on Biodiversity (COP16) in Rome has concluded with an agreement to adopt the first global plan for financing nature conservation, after three days of meetings. This meeting meant resuming the negotiations that began last October in Cali (Colombia), where the parties failed to reach an agreement on how to finance the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework reached at COP15, which aims to protect a third of the land and oceans by 2030.
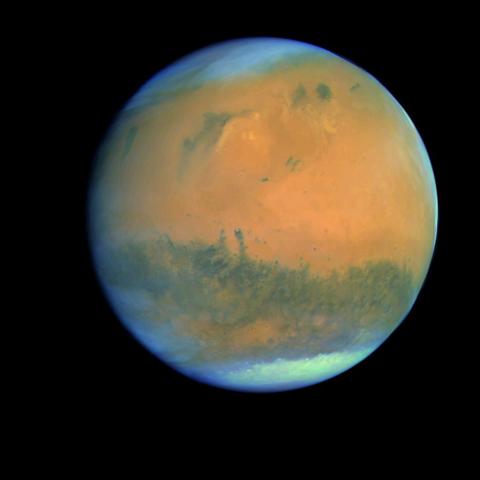

The red colour of Mars corresponds to a type of ferrihydrite that is the dominant form of iron oxide in Martian dust, although previous studies have attributed it to anhydrous haematite. The persistence of ferrihydrite, whose formation requires water, suggests that it formed during a cold, wet period, followed by a transition to the planet's current arid environment. The result, based on ESA and NASA space data and new laboratory experiments, is published in Nature Communications.

Aspartame, a common sweetener used in many sugar-free foods and drinks, affects the cardiovascular health of mice and monkeys, a study claims. Consuming aspartame increases the animals' insulin levels and contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries, according to the research article published in Cell Metabolism.
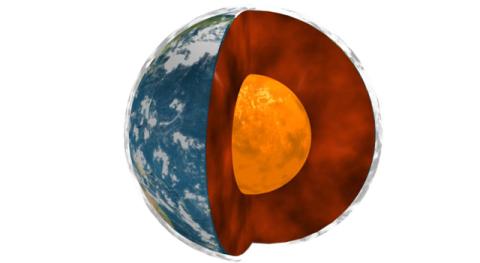
A study in 2024 described how the Earth's core had slowed down its rotation speed in recent decades. Now, the same international team of scientists adds that its shape has also changed over the last two decades. Until now, it was thought that both processes could not occur simultaneously. According to the researchers, who publish the results in the journal Nature Geoscience, the finding could improve our knowledge of the core's properties and structure.