
Complutense University of Madrid
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Lecturer of Palaeontology at the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM) and affiliated researcher at CENIEH
Professor of Prehistory and member of the Institute for Feminist Research at the Complutense University of Madrid
Associate Professor at Camilo José Cela University, researcher at the HM Hospitales Health Research Institute (Madrid) and collaborating researcher in the Department of Personality, Evaluation and Clinical Psychology at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Astrophysics and Director of the Space Astronomy Group at the Complutense University of Madrid
Acute Cardiac Care Unit Coordinator. Cardiovascular Institute. Hospital Clínico San Carlos. Madrid; Associate Professor of Medicine at Complutense University of Madrid; and President of the Association of Ischemic Heart Disease and Acute Cardiac Care of the Spanish Society of Cardiology
Accredited professor, lecturer at the Faculty of Psychology and director of the Research Group on Testimony Psychology at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Biochemistry at the Complutense University of Madrid, president of the Spanish Society of Dietetics and Food Sciences (SEDCA) and treasurer of the Spanish Federation of Nutrition, Food and Dietetics Societies (FESNAD).
Lecturer in the Department of Theoretical Physics and member of the Dynamics of Disordered Systems group at the Complutense University of Madrid
Professor of Animal Health at the Complutense University of Madrid and advisor to the WHO in the field of antibiotic resistance
Permanent professor at the TRANSOC Institute of the Complutense University of Madrid

A study has analyzed changes in the Earth's average global surface temperature over the past 485 million years and has discovered oscillations ranging from 11°C to 36°C, representing a variation of up to 25°C. The research concludes that temperatures during the Phanerozoic underwent more fluctuations than previously thought and shows a correlation between CO2 and changes in Earth's temperature. The article, published in the journal Science, combines thousands of data points with a modeling method used for weather forecasting.

Hormonal therapy to treat breast cancer is associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in women over 65, a study says. The retrospective analysis is based on data from more than 18,000 women with breast cancer in the US: two-thirds of them had received hormone therapy and one-third had not. The "protective effect" of hormone therapy declines with age and varies by ethnicity, adds the article published in JAMA Network Open.

Five out of ten potential treatments move from animal studies to human studies; four to randomised controlled clinical trials; and one in 20 moves on to approval by regulatory agencies, an analysis estimates. Concordance between positive results in animals and in clinical studies is 86%, according to the study, published in PLoS Biology, which pools the findings of 122 published studies on 54 different human diseases.

ESA's ExoMars and Mars Express missions have for the first time detected ice near the equator of Mars, specifically in the Tharsis volcanoes, an area of the planet where it was thought impossible to exist. According to the researchers, who publish the results in the journal Nature Geoscience, such findings are important for habitability and future human exploration.

According to a report published yesterday in The New York Times, most of the members of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy had rejected the proposal to declare the beginning of the Anthropocene, thus showing their opposition to the idea that this is a new geological epoch. Other sources told El País that the result of the vote was not formally confirmed. If this proposal is defeated, the process could be restarted from scratch at a later date.
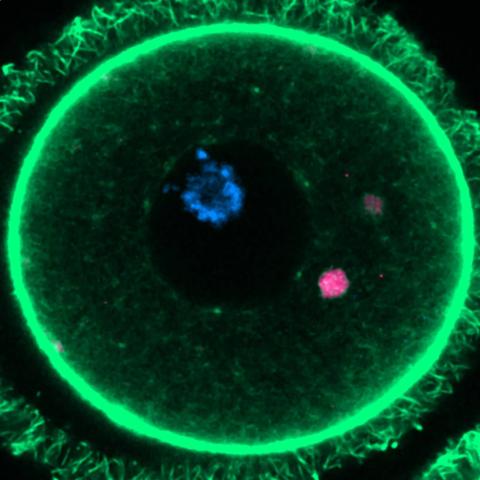
At an informative meeting organized by the Science Media Centre Spain, the coauthor of a paper published this week in the journal Cell discussed his findings with journalists. Although the study was conducted with mice, he is confident in being able to analyze human eggs to see if his conclusions could explain the loss of fertility that occurs in women with age.
An international team, led by a Spanish group, has published the mechanism that allows immature egg reserves (oocytes) to survive for many years, up to almost half a century in the case of humans. The research studies how oocytes are affected by protein aggregates similar to those that damage other cells such as neurons and can cause neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. The finding of how these egg reserves are kept healthy may help to understand some causes of infertility. The results are published in the journal Cell.

This week, Spain’s Ministry of Health launched a process to develop a Royal Decree on the medical use of cannabis, assuring that it will be "a rigorous measure based on the best scientific evidence available.” The goverment is conducting a public consultation until 4 March to gather the opinions of citizens, civil society organisations, professional associations and scientific societies. In this explainer, we attempt to answer the main questions that arise regarding the medical use of cannabis.
A team of researchers has demonstrated how a non-invasive ultrasound technique can increase the movement of human sperm in the laboratory by up to 266%. Using microfluidic droplets to evaluate individual sperm cells, which had not been done before, they found that ultrasound exposure induced movement in immobile sperm and improved swimming speeds in mobile ones. The work is published today in the journal Science Advances.

In an anonymous online survey of dog owners in Denmark, 38% of respondents said they administered cannabinoid products - such as cannabidiol drops - to their pets without a prescription, even though their use is not legal in animals. Reasons given included pain, behavioural problems and allergies in their dogs. Some 2,000 people responded to the survey, the results of which are published in the journal PLoS ONE.