
University of Oviedo
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Ramón y Cajal researcher in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of the University of Oviedo.
Researcher at the Mixed Institute for Biodiversity Research (IMIB), CSIC-University of Oviedo-Principality of Asturias
Assistant Professor in the Department of Philosophy at the University of Oviedo, where she is a member of the Research Group on Social Studies of Science and Technology (CTS Group).
Permanent lecturer in the Department of Philosophy, University of Oviedo
Senior scientist at the CSIC and head of the Department of Biodiversity and Global Change of the Joint Institute for Biodiversity Research (University of Oviedo-CSIC)
Full Professor at the University of Oviedo in the area of “Computer Languages and Systems”
Researcher in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Member of the Department of Neurology, Stroke Unit of the Central University Hospital of Asturias (HUCA) and Associate Professor of Health Sciences, University of Oviedo
Researcher at the Joint Institute for Biodiversity Research of the University of Oviedo
Full professor of Pathological Anatomy at the University of Oviedo, Scientific Director of the Principality of Asturias Biobank (BioPA) and Coordinator of the Organoid hub of the ISCIII Biomodels and Biobanks platform

The collision between two high-speed trains in Adamuz (Córdoba) on Sunday afternoon has left at least 39 people dead and more than a hundred injured. The emotional impact of the accident affects the families of the victims, as well as the crash survivors and other train users.

An international report led by the University of Cambridge (United Kingdom) warns that there is a serious risk of a ‘lost’ generation emerging in Gaza, due to the combination of educational, physical and psychological impacts after more than two years of the Israeli invasion. As of 1 October 2025, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) reported the deaths of 18,069 students and 780 education personnel in Gaza, with 26,391 students and 3,211 teachers injured. The study estimates that children in Gaza will have lost the equivalent of five years of education due to repeated school closures since 2020, first due to COVID-19 and then due to the Israeli invasion.

Two research teams, with some authors in common, have shown in two separate studies that interaction with chatbots using artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly change a voter's opinion about a presidential candidate or a policy proposal. One of the studies, published in Nature, was conducted in three countries (the US, Canada, and Poland), while the other, developed in the UK, is published in Science. Both studies reach the same conclusion: the persuasive power of these tools stems less from psychological manipulation than from the accumulation of fact-based claims that support their position. However, this information is not always accurate, and the greater the persuasive power, the greater the inaccuracy and fabrication.

A US research team has devised a method that uses a browser extension to alter the algorithm of X (formerly Twitter) to study its impact on user behaviour. In a 10-day experiment with 1,256 volunteers during the 2024 US presidential campaign, they used the method to vary the content expressing anti-democratic attitudes and partisan hostility. According to the authors, the results—published in Science—provide causal evidence that greater or lesser exposure to this type of content alters polarisation in the same way. Their conclusions contradict previous research published in the same journal, which found no such relationship on Facebook or Instagram. In that case, the study was conducted in collaboration with and funded by Meta.

Consuming up to four cups of coffee a day is associated with an increase in telomere length in people with severe mental disorders, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Telomere length is an indicator of cellular ageing and is shorter in people with these disorders, although the causes are not clearly understood. According to the study, published in BMJ Mental Health, the effect shown is comparable to ‘a biological age five years younger’ in coffee drinkers.

A new article published in eClinicalMedicine measures mental health problems in the Gaza Strip among the population over 40 years of age before and after the genocide committed by Israel. The study indicates that the proportion of these adults experiencing high levels of distress has tripled in the last five years, with a peak following the escalation of the massacre since October 2023. It was already known that chronic stress factors affecting victims pose a serious threat to mental health, but no longitudinal study had yet been conducted comparing distress in the same individuals before and after the genocide.

A study by the University of Cádiz has identified six factors that drive polarization around health-related issues, for example during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic: political ideology, misinformation, social media dynamics, trust in institutions and professionals, risk perception, and socioeconomic factors. This review, published in Science Advances, brings together the conclusions of 90 previous studies and analyzes how these determinants exacerbate health inequalities and influence compliance with public health measures.
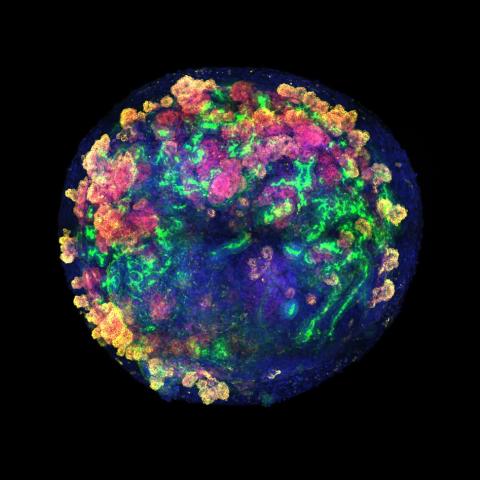
An international team, including several Spanish groups and coordinated by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), has developed a pioneering technology that allows for the creation of multiple human kidney organoids, their combination with pig kidneys outside the body, and their successful transplantation back into the same animal. The method could contribute to improving future research and, according to the authors, allows us to envision a future clinical scenario in which organs destined for transplantation can be treated and conditioned before implantation. The work is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.

A team from China has reported the results of the first liver transplant from a pig to a living human. Earlier this year, a procedure that served as a proof of concept was published, but it was performed on a brain-dead person. In this case, after modifying 10 genes in the porcine liver, an auxiliary transplant—not removing the entire organ—was performed on a 71-year-old patient with cirrhosis and liver cancer. It worked well for the first month, but on day 38, the graft had to be removed due to the development of complications, and the patient died on day 171. According to the researchers, who published the case in the Journal of Hepatology, this is "a fundamental step that demonstrates both the promise and the obstacles that remain to be overcome".
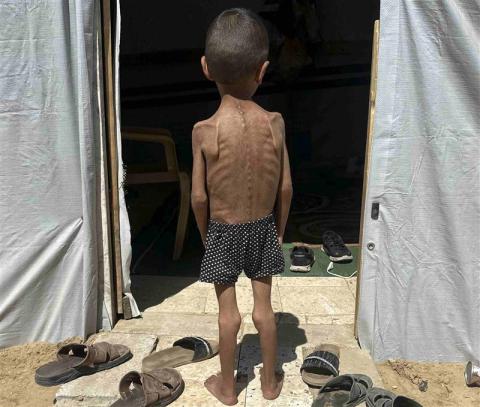
More than 54,600 children under the age of five in Gaza are in need of medical care for acute malnutrition, according to estimates from a study published in The Lancet, which shows that the prevalence of malnutrition decreases during a ceasefire and increases during Israeli blockades of access to food, water, or medicine. For example, after four months of severe aid restrictions—between September 2024 and January 2025—malnutrition increased from 8.8% to 14.3%, with a higher incidence in Rafah and among children between 24 and 59 months of age. The study, conducted by UNRWA, is based on data from more than 219,000 children between the ages of six and 59 months from various locations in the Gaza Strip, collected between January 2024 and August 2025.