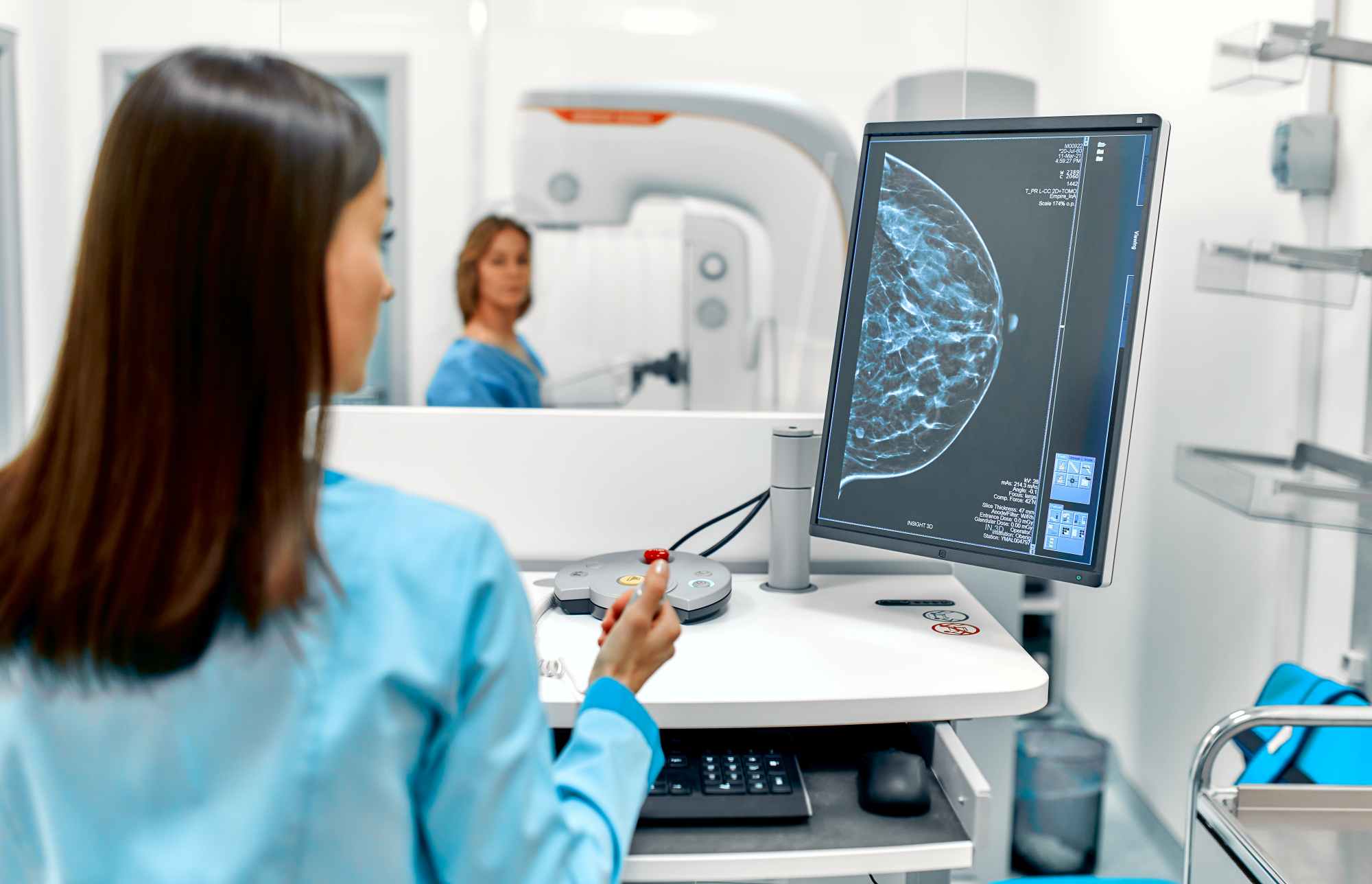
Adults who use Instagram a lot overestimate its “addictive” nature, making self-control difficult dificulta el autocontrol
A study published in Scientific Reports concludes that adults who use Instagram very frequently overestimate their ‘addictive’ use, which complicates self-control and increases feelings of guilt. According to the research, excessive use, in most cases, is not an addiction but a habit. The study was conducted on more than 1,000 Americans and suggests that the fact that many think they have an ‘addiction’ may be related to the media's frequent use of this term when talking about social media.