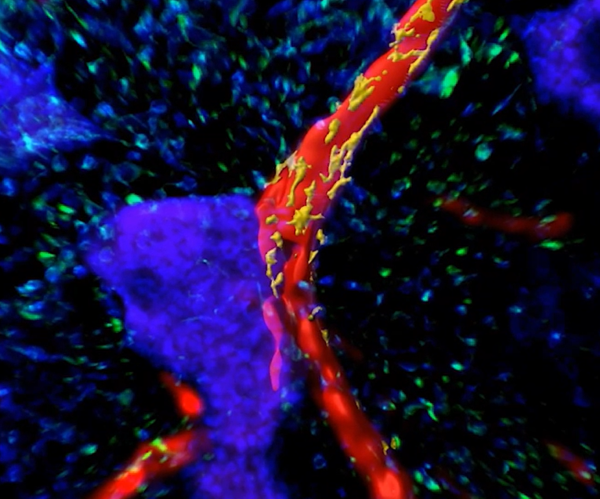
Tiny organoids help repair liver damage in mice
Japanese scientists have developed tiny liver organoids from stem cells that, transplanted into mice, integrate with the original organ and help repair fibrotic lesions. This scar-like tissue damage is common to many liver diseases, such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. According to the authors, who publish their results in the journal Science Translational Medicine, such organoids could offer an alternative to liver transplants in the future.