
University of Extremadura
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Professor of Physiology at the University of Extremadura (UEx), Neuroimmunophysiology and Chrononutrition group.
Substitute lecturer and researcher at the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences of the University of Extremadura
Professor of Physical Education in the Faculty of Teacher Training at the University of Extremadura
Head of the Environmental Radioactivity Laboratory
Member of the working group of the European Academies' Science Advisory Council (EASAC) author of the report, member of the science and technology advisory group (E-STAG) of the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR), retired professor at the University of Extremadura, member of the Academia Europaea (The Academy of Europe) and associate researcher at the Institute for Studies on Conflicts and Humanitarian Action (IECAH).

Menstrual cycles were synchronised with lunar cycles until 2010, but according to research published in Science Advances, after this date, this synchrony is only found in January, when lunar gravity is at its strongest. The team analysed the menstrual records of 176 women and attributes the loss of synchrony to the increasing use of smartphones and LED night lights, which became widespread from 2010 onwards.

Extreme wildfires are becoming more frequent and causing greater environmental and social impact. Current policies that prioritise fire suppression have not only failed to prevent this situation from arising, but actually made it worse. The report Changing Wildfires - Policy Options for a Fire-literate and Fire-adapted Europe, released by the European Academies' Science Advisory Council (EASAC), addresses this issue by outlining eight policy options. The report's key recommendations focus on putting landscape management first —by regulating biomass structure and land use — and empowering local communities.

A team in the United States has analysed how exposure to environmental chemicals in previous generations influences the onset of the first menstruation. The researchers used data from the California Child Health and Development Study (CHDS) and analysed blood samples taken from 250 pairs from the 1960s. The results, presented at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society in San Francisco (USA), show that although the average age of first menstruation remained stable between grandmothers and their daughters, it decreased by one year between daughters and granddaughters. Certain chemicals present in the blood of the mother and father were linked to the onset of puberty in their descendants, with stronger effects in granddaughters, according to the study, and with greater weight of male exposure.
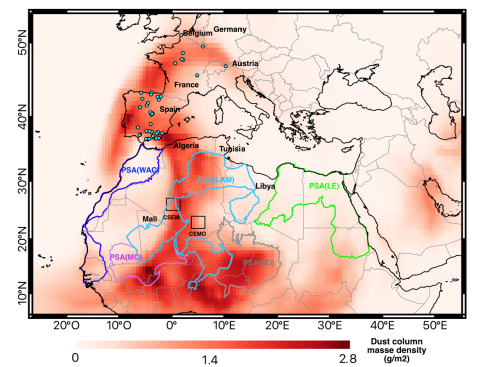
The Saharan dust intrusion that reached Spain and other European countries in March 2022 posed no risk to human health in terms of exposure to radioactivity, according to an analysis of samples collected by citizens in Spain, Germany, Austria, Belgium, France, Belgium, France, and Luxembourg. The dust came from southern Algeria, says the analysis published in Science Advances, and contained plutonium isotopes characteristic of nuclear tests conducted by the U.S. and the Soviet Union - not from French tests in the Reggane area in the 1960s.
Artemisinins, plant-based antimalarials, may serve as a treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome - which affects millions of women worldwide and can lead to infertility - according to a new study published in Science. The compounds suppressed ovarian androgen production in rodents, as well as in a small cohort of 19 human patients for 12 weeks, leading to more regular menstrual cycles without side effects.

Research published in JAMA Network Open indicates that women with premenstrual disorders diagnosed before the age of 25 have a higher risk of all-cause mortality and death by suicide. For death by suicide, the risk increased regardless of age at diagnosis. However, in general, women with premenstrual disorders do not have an increased risk of premature death from natural and unnatural causes. The study compares over several years a group of more than 67,000 women in Sweden with a diagnosed disorder with a group of more than 338,000 women without such a diagnosis.

The ovarian cycle is regulated by internal circadian rhythms rather than external processes, says a study published in Science Advances. Using menstrual cycle data from some 3,000 women in Europe and North America, the authors add that the influence of the lunar cycle on women's menstrual cycle is weak, but significant.

Dressing in school uniform is associated with less physical activity in children, especially primary school girls, according to a study by the University of Cambridge (UK) published in the Journal of Sport and Health Science. The study analysed data on the physical activity levels of more than one million children aged 5-17 in 135 countries, including Spain, combined with an online survey.

Results from a survey of more than 39,000 menstruating individuals reveal that 42% experienced heavier bleeding after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Among the most likely groups were pre-menopausal women, Hispanic or Latina women, those who had been pregnant, and those with conditions such as endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome.