Spanish Society of Epidemiology
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Professor of Preventive Medicine and Public Health at the University of Barcelona and member of the Spanish Society of Epidemiology
Professor of Preventive Medicine and Public Health at the Autonomous University of Madrid, President of the Nutrition and Obesity Study Observatory (NAOS), and member of the Nutrition Group of the Spanish Society of Epidemiology
Secretary of the Spanish Society of Epidemiology
Screening Coordinator at Osakidetza -Basque Health Service, researcher in the Cancer Biomarkers group at the Biobizkaia Health Research Institute, and secretary of the Board of Directors of the Spanish Epidemiology Society
Co-coordinator of the working group on Nutrition of the Spanish Society of Epidemiology (SEE), Professor of Preventive Medicine and Public Health at the University of Navarra, and member of CIBERobn
Professor of Preventive Medicine and Public Health at the University of Valencia and outgoing president of the Spanish Society of Epidemiology (SEE).

An international report led by the University of Cambridge (United Kingdom) warns that there is a serious risk of a ‘lost’ generation emerging in Gaza, due to the combination of educational, physical and psychological impacts after more than two years of the Israeli invasion. As of 1 October 2025, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) reported the deaths of 18,069 students and 780 education personnel in Gaza, with 26,391 students and 3,211 teachers injured. The study estimates that children in Gaza will have lost the equivalent of five years of education due to repeated school closures since 2020, first due to COVID-19 and then due to the Israeli invasion.

Three articles with Spanish participation, published in The Lancet, review the evidence that ultra-processed foods are worsening diet quality and displacing the consumption of fresh and minimally processed foods. Furthermore, they warn that their consumption is linked to a higher risk of multiple chronic diseases. According to the authors, who also review the associated policies and commercial factors, only a coordinated global response can combat the strategy of the companies that market these products.
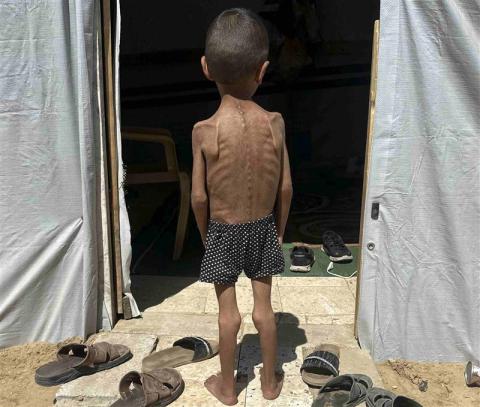
More than 54,600 children under the age of five in Gaza are in need of medical care for acute malnutrition, according to estimates from a study published in The Lancet, which shows that the prevalence of malnutrition decreases during a ceasefire and increases during Israeli blockades of access to food, water, or medicine. For example, after four months of severe aid restrictions—between September 2024 and January 2025—malnutrition increased from 8.8% to 14.3%, with a higher incidence in Rafah and among children between 24 and 59 months of age. The study, conducted by UNRWA, is based on data from more than 219,000 children between the ages of six and 59 months from various locations in the Gaza Strip, collected between January 2024 and August 2025.

Through surveys of 78 healthcare workers in Gaza between August 2024 and February 2025, an international team has documented patterns of injuries among the civilian population during Israel's ongoing invasion. The most common traumatic injuries were burns, followed by injuries to the lower and upper limbs. Explosion damage accounted for most of the weapon-related trauma, which particularly affected the head, while gunshot wounds were mainly located in the lower limbs. The study is published in The BMJ.

On 22 August, the UN officially declared famine in Gaza, defined as an extreme situation of food insecurity in which there is insufficient access to food to survive, leading to high rates of malnutrition, disease and mortality. The Spanish Society of Epidemiology explains how this situation is technically assessed, as well as the implications of the declaration.

Consumption of ultra-processed food is associated with an increased likelihood of having prodromal signs of Parkinson's disease - symptoms that precede the disease - says a study published in Neurology. The analysis is based on data from more than 42,000 healthcare professionals in the US, followed for up to 26 years.
A study published today in Nature with the participation of the CNIO points to the bacterial toxin colibactin, produced by some strains of Escherichia coli, as a possible culprit in the increase in early-onset colorectal cancer. The study shows that exposure to the toxin during early childhood leaves a genetic signature in colon cells and demonstrates a substantial increase in these mutations in cases of colorectal cancer in people under 50.

Consuming certain mixtures of common food additives is linked to a slightly increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to an analysis of data from more than 108,000 adults in France. The study, published in PLoS Medicine, identified five mixtures of additives frequently used in ultra-processed foods and concluded that two of them are associated with the disease: the first mixture consisted mainly of emulsifiers, preservatives and a colouring agent, and the second of acidifiers, acidity regulators, colouring agents, artificial sweeteners and emulsifiers.

Today the Spanish Parliament rejected the creation of the State Public Health Agency, a proposal that had been envisaged since the Public Health Act of 2011 and whose idea of implementation had resurfaced after the pandemic.

From 2011 to 2019, improvements in life expectancy slowed down in many European countries and many experienced declines in this indicator during the Covid-19 pandemic (2019-2021), according to a study published in The Lancet Public Health. The research shows that the average annual improvement in life expectancy fell from 0.23 years (1990-2011) to 0.15 years (2011-2019) in 20 European countries, including Spain.