Candida auris infections in Spain are the highest in Europe over the last decade, according to an ECDC report
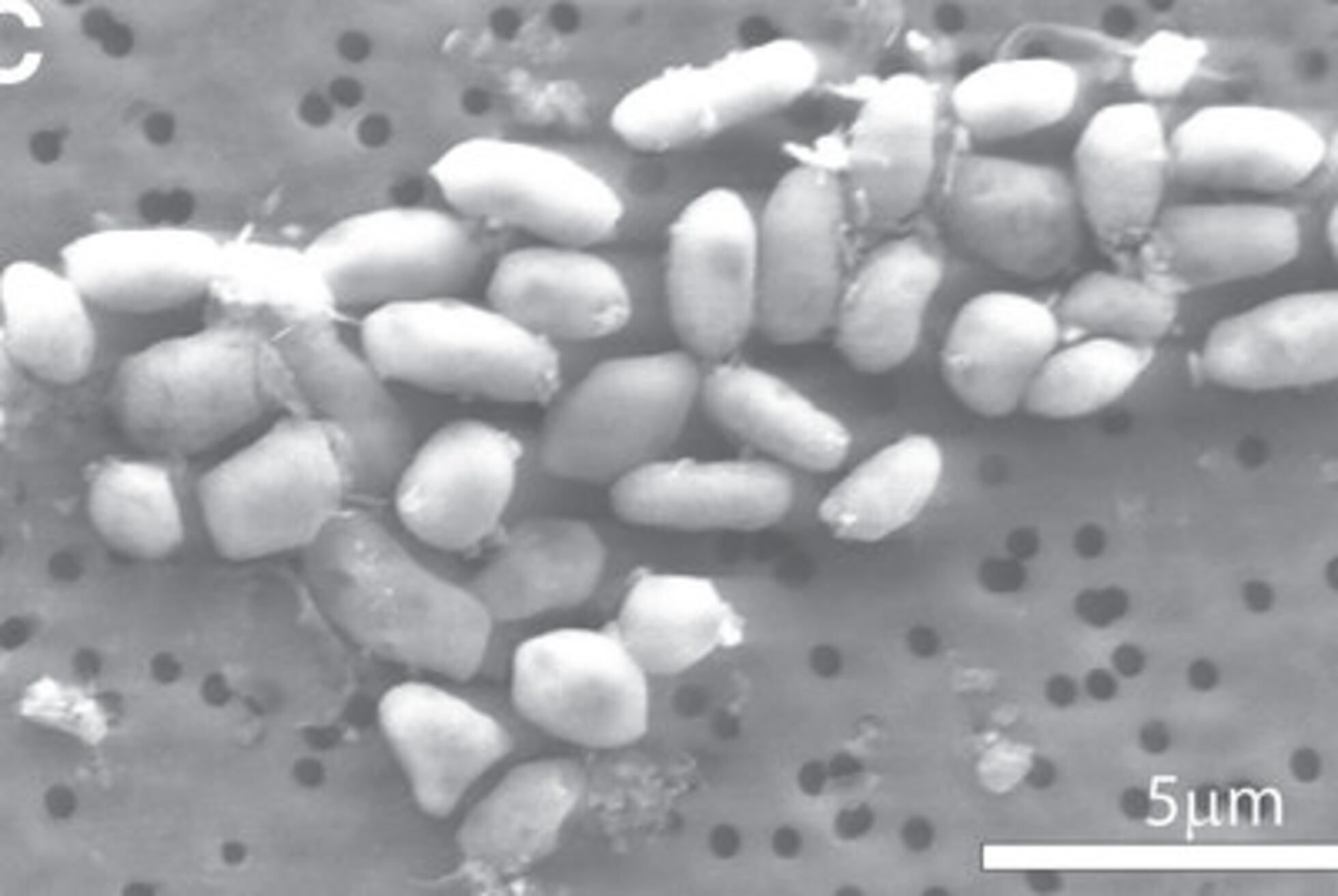
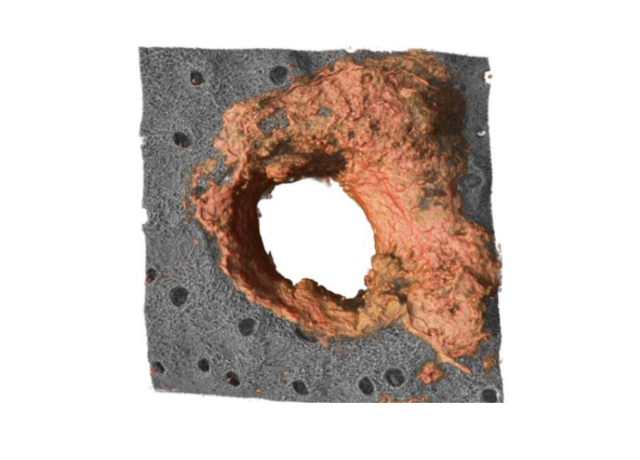
Infections caused by the fungus Candidozyma auris—formerly known as Candida auris—continue to rise, warns a report by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Spain reported 1,807 of the 4,012 cases in 36 European countries between 2013 and 2023, the highest number ahead of Greece (852 cases) and Italy (712), according to the survey. This microorganism spreads particularly in hospitals, causing infections that are often resistant to existing drugs.