Molecular profile of the Spanish supercentenarian who became the oldest person in the world analysed
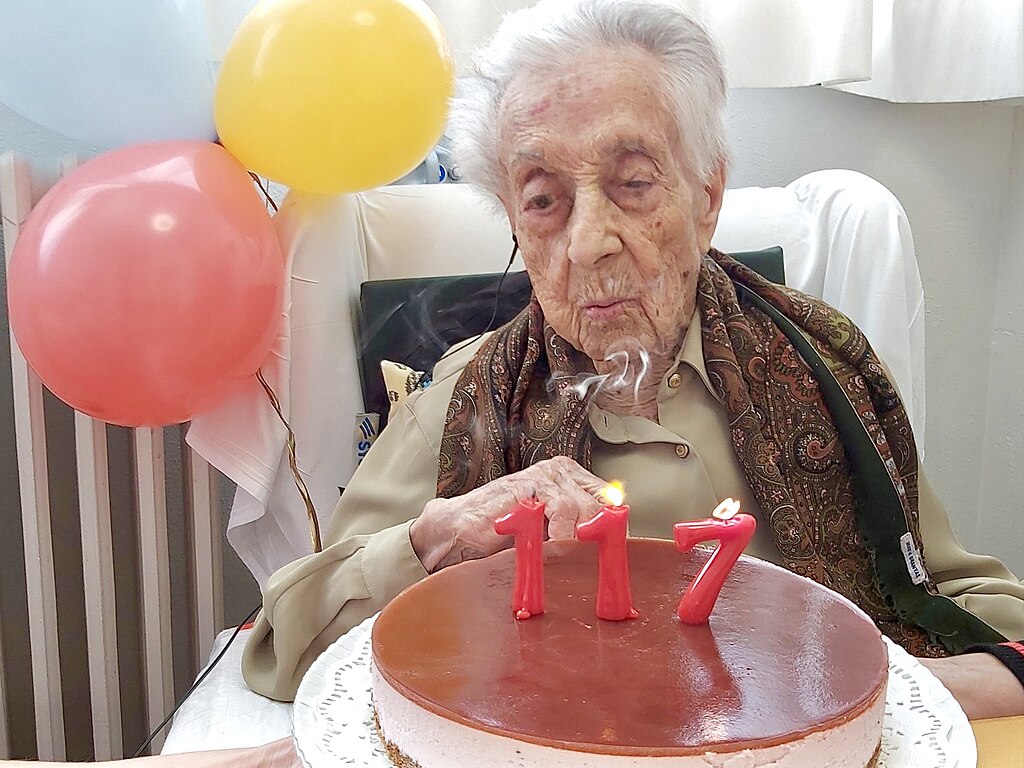
Maria Branyas was considered the oldest person in the world when she died in 2024 at the age of 117. An international team led by the Cancer Epigenetics group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute and the University of Barcelona has analysed her molecular profile, including her genome, metabolome, microbiome and epigenome. "Our results have helped us identify factors that could help many older people live longer, healthier lives," say the researchers, whose work is published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.