Neutrophils that reinforce the physical barrier of the skin discovered
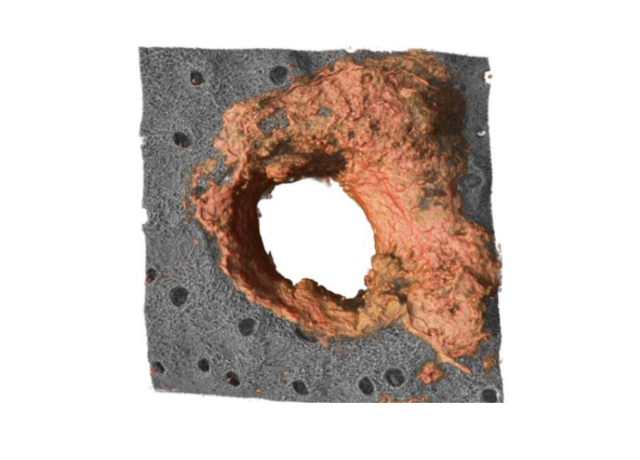
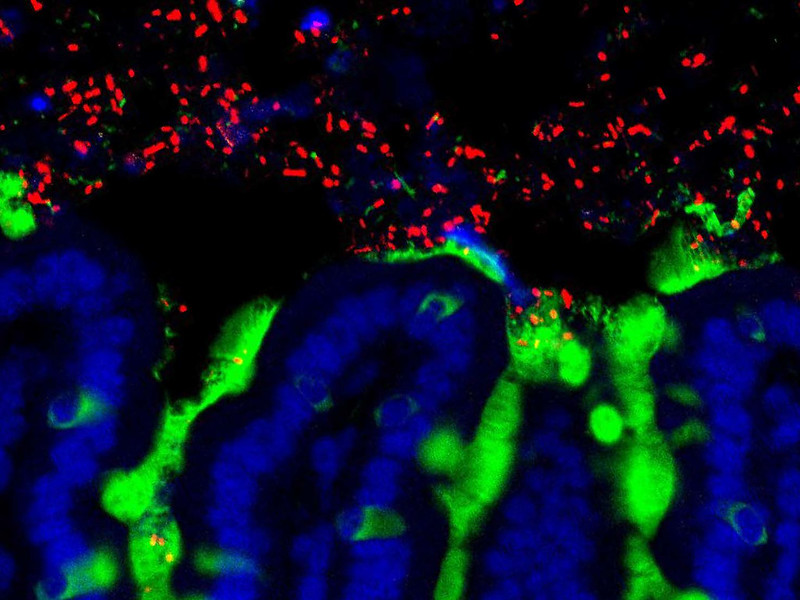
A CNIC research team has identified a population of skin neutrophils that reinforce the physical protection of the tissue against infection. These immune cells are known for their microbicidal role, and the study published in Nature reveals that they also produce an extracellular matrix that reinforces the physical barrier of the skin.