Deep brain stimulation improves walking after spinal cord injury
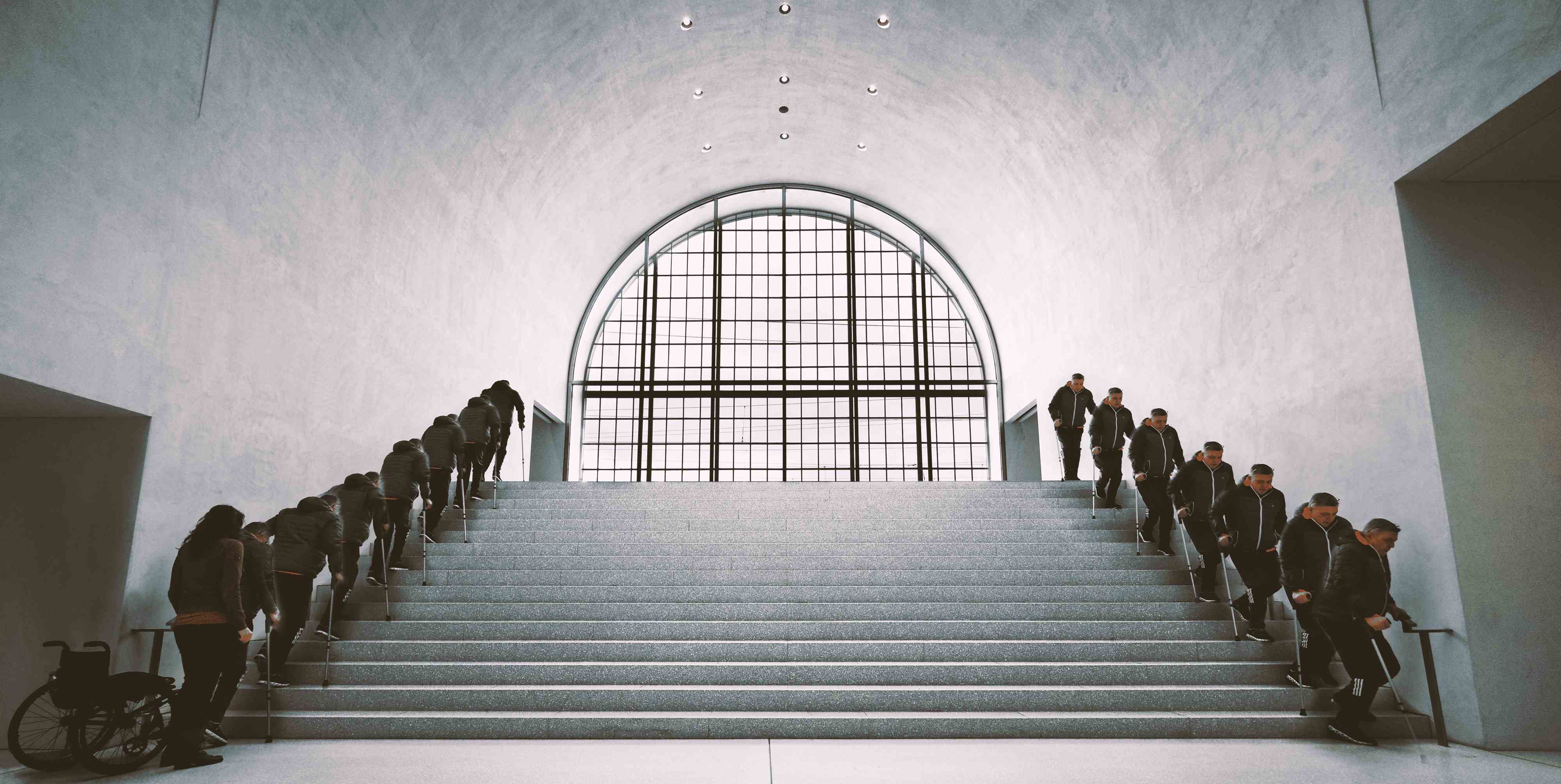
According to a study published in Nature Medicine, deep brain stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus improves walking and promotes recovery in humans and rodents with spinal cord injuries. In humans, the authors tested this technique on two patients who relied on assistive devices and had difficulty walking; both showed improved performance in the ten-meter and six-minute walking tests. Combined with rehabilitation, the patients experienced recovery that persisted even after the deep brain stimulation was turned off.