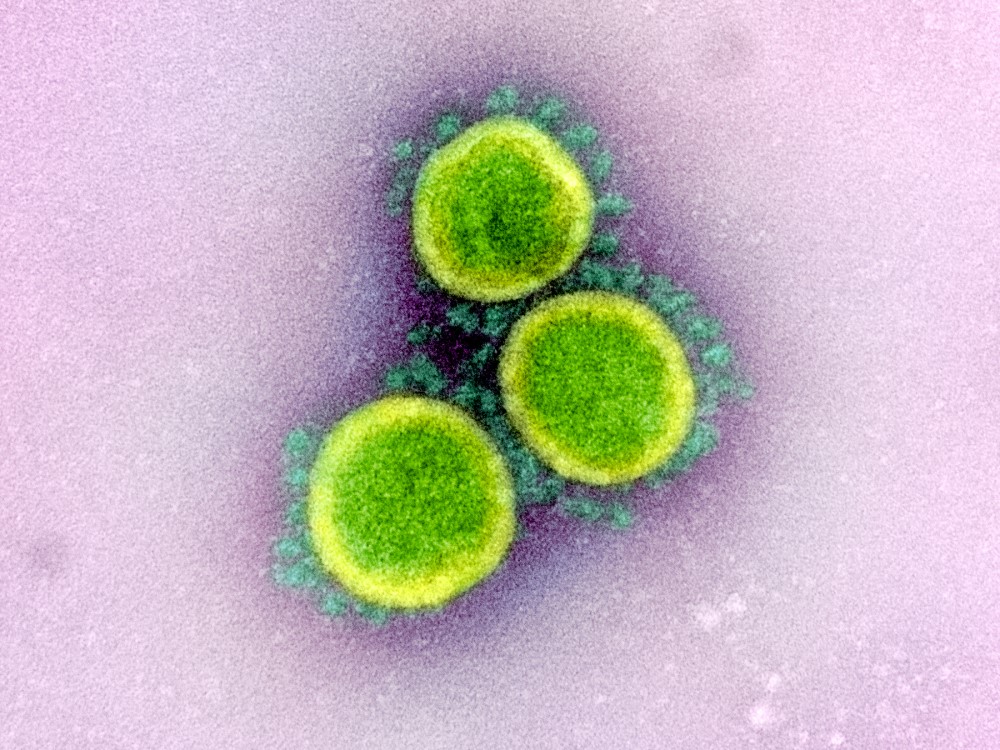
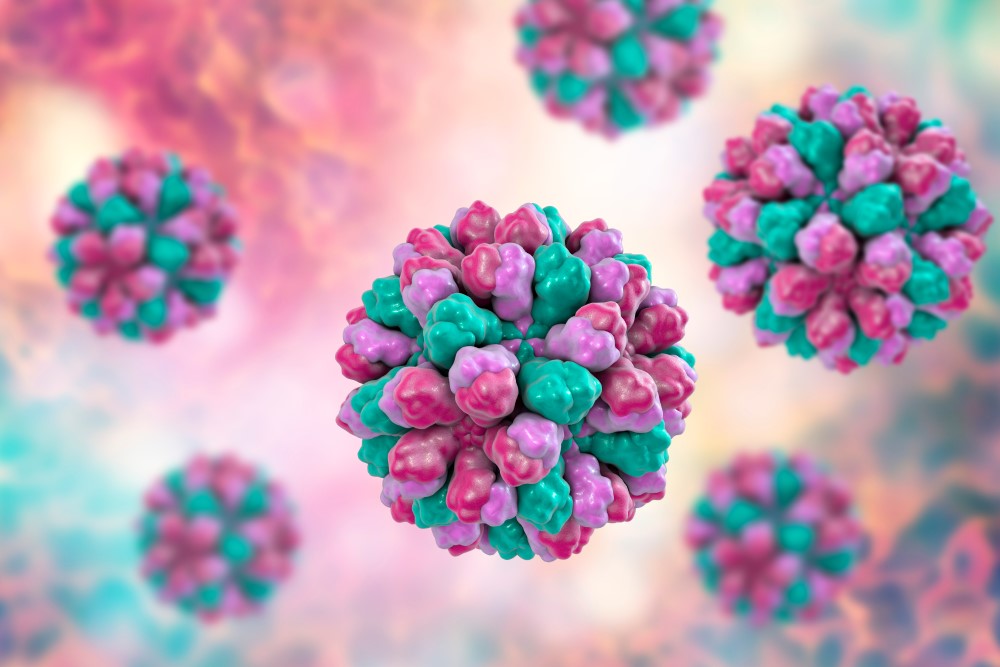
The nostrils defend us against rhinovirus and determine the severity of the infection
When a rhinovirus, the most common cause of the common cold, infects the lining of our nasal passages, cells work together to fight it off by activating an arsenal of antiviral defences. An article published in the journal Cell Press Blue demonstrates how they do this and suggests that it is the body's defences, rather than the virus itself, that determine whether we catch a cold or not, as well as the severity of the symptoms.