A report highlights the risks of misuse of data collected by menstrual apps
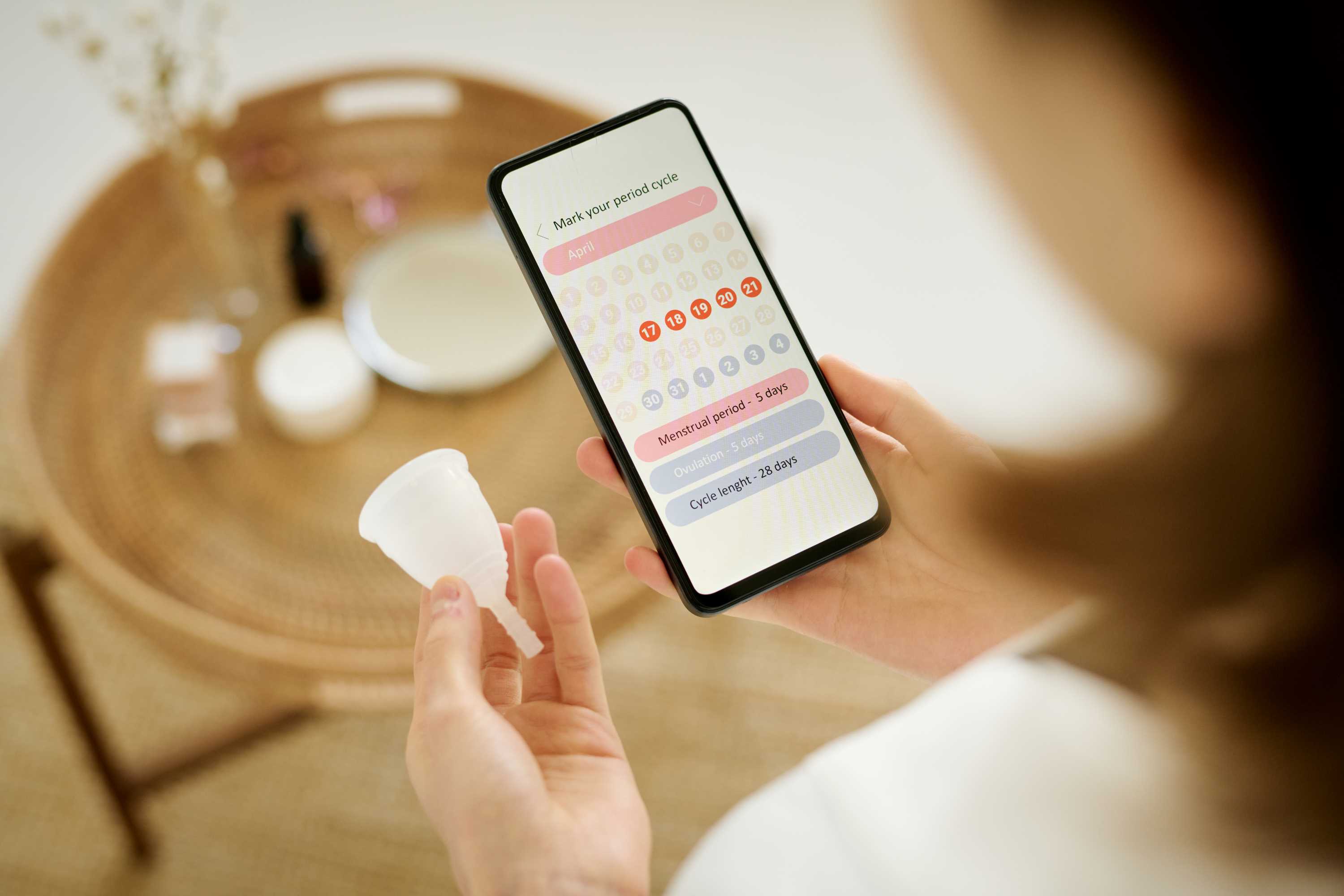
Menstrual cycle tracking apps pose risks to users, according to a report published by the Minderoo Centre for Technology and Democracy at the University of Cambridge (United Kingdom). These apps collect intimate data about their users' physical and mental health and reproductive decisions, which can be exploited for commercial or legal purposes, the report warns.