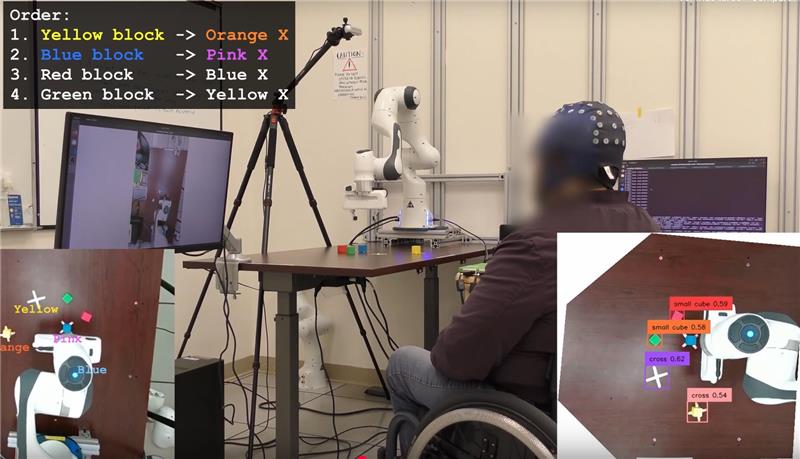
Online images and texts portray women as less experienced than men across all occupations
On the internet, professional women are represented as younger—and therefore less experienced—than their male counterparts, even though this age difference does not correspond to actual data in the US, according to an article published in Nature. This study of gender and age stereotypes is based on an analysis of 1.4 million images on five platforms (Google, Wikipedia, IMDb, Flickr and YouTube), as well as nine large language models, such as ChatGPT, trained with texts from Reddit, Google News, Wikipedia and Twitter.