
Severo Ochoa Centre for Molecular Biology, UAM-CSIC
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Scientific researcher at the CSIC at the Severo Ochoa Center for Molecular Biology
Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the Autonomous University of Madrid and deputy director of the Centre for Molecular Disease Diagnosis at the Centre for Molecular Biology (CBM-UAM-CSIC).
Senior Scientist at the CSIC and researcher at the Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa
Professor ad honorem of the CSIC at the Severo Ochoa Centre for Molecular Biology
Virologist and immunologist at the Severo Ochoa Centre for Molecular Biology, coordinator of the CSIC interdisciplinary research platform on Global Health.
Head of the Pathogenic Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease research group and researcher at the Severo Ochoa Molecular Biology Centre
Senior Researcher at the Severo Ochoa Center for Molecular Biology (CBM-CSIC-UAM)
Head of the Immunometabolism and Inflammation Laboratory at the Center for Molecular Biology and scientific researcher at the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
Principal investigator at the Severo Ochoa Molecular Biology Centre
Head of the African Swine Fever Virus Laboratory at the Severo Ochoa Molecular Biology Center (CBMSO)

The sequencing of the DNA of the virus found in wild boars infected with African swine fever in Catalonia and its comparison with the DNA of 17 of the 19 samples being investigated at the Animal Health Research Centre (IRTA-CReSA) has revealed that they do not match, according to a press conference held this morning by representatives of the scientific team in charge of the study and the Catalan Regional Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries. They consider the leak from the laboratory to be ‘highly unlikely’, although further studies are still ongoing. The research, led by the IRB, suggests that it could belong to a new strain not described in the scientific literature.

The veterinary services of the Catalan Regional Government have notified the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Food of the detection of two wild boars positive for African swine fever virus in Bellaterra (Barcelona), where they were found dead on November 26. These cases represent the first detection of the disease in Spain since November 1994, according to the ministry in a press release. African swine fever is considered a Category A disease by the European Union, which means that member states must take measures to control and eradicate it as soon as possible. It is a non-zoonotic disease, meaning that humans are not susceptible to infection either through contact with animals or through the consumption of animal products.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell and Shimon Sakaguchi for describing how the immune system is regulated so as not to harm us. His groundbreaking discoveries on peripheral immune tolerance have spurred the development of new treatments for cancer and autoimmune diseases.
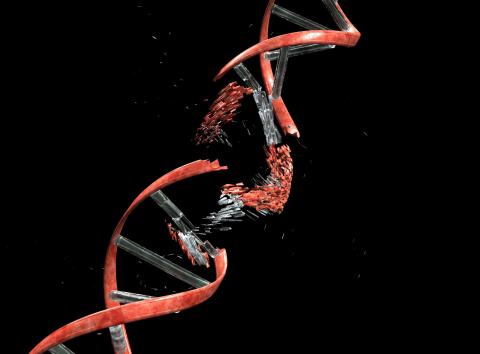
The very functioning of the cell itself or stresses such as those caused by sun exposure can cause breaks in our DNA, which must be repaired. A study developed by the CNIO has completed a catalog of how each of our genes affects the repair of some of these breaks and how they influence the resulting "scars." The catalog, which they have called the "human repairome," will be openly available. According to the researchers, whose work is published in Science, it will have "implications for human health, including the biology and treatment of cancer, as well as for efforts toward total control of CRISPR-Cas gene-editing technologies".
An international team has analysed gender representation in more than 1,000 clinical trials on cardiovascular disease between 2017 and 2023, involving more than one million people. Although female participation has increased, especially in areas such as obesity and heart failure, women continue to be underrepresented overall compared to men. The results, presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress held in Madrid from 29 August to 1 September, are published in JAMA Network Open.
A team from Sweden has analysed post mortem brain samples from people aged between 0 and 78 using various techniques and found that, although it varies between individuals, new neurons continue to form in the hippocampus with no apparent age limit. Although previous studies had reached similar conclusions, controversy remains about these results. According to the authors, the new work ‘provides an important piece of the puzzle in understanding how the human brain works and changes throughout life.’ The results are published in the journal Science.
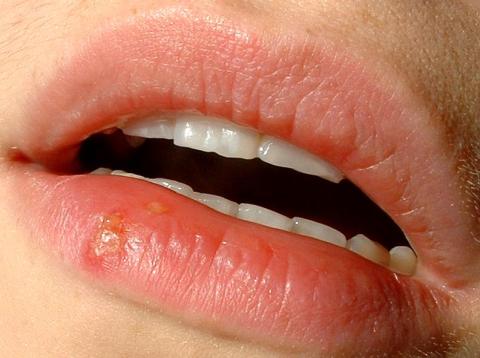
A US study analysing data from nearly 700,000 people concluded that those with a history of herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) infections were at greater risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. The study, published in BMJ Open, also showed that patients with this virus who used anti-herpes treatments were less likely to develop the disease.

Researchers in China have analysed data from more than 4,500 people and identified 13 proteins linked to brain ageing. In addition, changes in protein concentrations in the blood tend to peak at ages 57, 70 and 78. According to the authors, who publish the results in the journal Nature Aging, these ages may reflect transitions in human brain health at specific ages, and could therefore be important for designing possible interventions in the brain ageing process.
The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman for their groundbreaking discoveries, which have radically changed our understanding of how mRNA interacts with our immune system, and made it possible to develop vaccines at unprecedented speed during the covid-19 pandemic.

Taurine is one of the most abundant amino acids in animals. As reported in research published in Science, its loss may contribute to the ageing process. According to the study, reversing age-associated taurine deficiency through supplementation improved life expectancy in worms and rodents, while improving some health parameters in non-human primates, which the authors believe would warrant further human trials to examine its effect on life expectancy and the potential risks involved.