Andalusian Centre for Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine (CABIMER)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Professor of Genetics at the University of Seville and head of the Genomic Instability and Cancer group at the Andalusian Center for Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine (CABIMER)
Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Seville, principal investigator at CABIMER (CSIC-US) in the Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Neuroimmunology
The very functioning of the cell itself or stresses such as those caused by sun exposure can cause breaks in our DNA, which must be repaired. A study developed by the CNIO has completed a catalog of how each of our genes affects the repair of some of these breaks and how they influence the resulting "scars." The catalog, which they have called the "human repairome," will be openly available. According to the researchers, whose work is published in Science, it will have "implications for human health, including the biology and treatment of cancer, as well as for efforts toward total control of CRISPR-Cas gene-editing technologies".
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterised by progressive loss of motor neurons. An international team has discovered evidence that ALS may have an autoimmune component, meaning that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, a hypothesis that had been considered by the scientific community. The study shows that inflammatory immune cells—called CD4+ T cells—attack certain proteins that are part of the nervous system in people with ALS. ‘These findings highlight the potential of therapeutic strategies aimed at improving regulatory T cells,’ the authors note in the research, published in Nature.

Researchers in the United States have used stem cells created from patients with a very rare type of ALS, more prevalent in Brazil, to target a key gene in the stress response and reverse the damage suffered by motor neurons in the laboratory. They believe it is "a promising proof-of-concept for future therapeutic strategies" and "could help lay the foundation for genetically informed clinical trials".
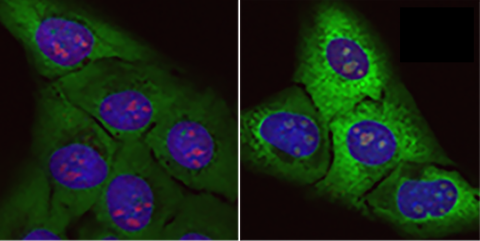
In a paper published in Molecular Cell, a team of researchers led by the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) provides the first evidence that a possible cause of the hereditary type of ALS - familial ALS - is the accumulation in motor neurons of 'junk proteins', proteins with no function that accumulate unduly and prevent the cell from functioning properly. In addition, the research describes a new causal factor in the ageing process: nucleolar stress, which encompasses alterations in organelles called nucleoli.

The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended granting marketing authorisation in the European Union for a new therapy for the treatment of adult patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a rare and frequently fatal disease that causes muscle weakness and leads to paralysis. Qalsody (tofersen) is indicated for the treatment of adults with ALS who have a mutation in the SOD1 gene. There is currently only one treatment for ALS authorised in the EU (riluzole).