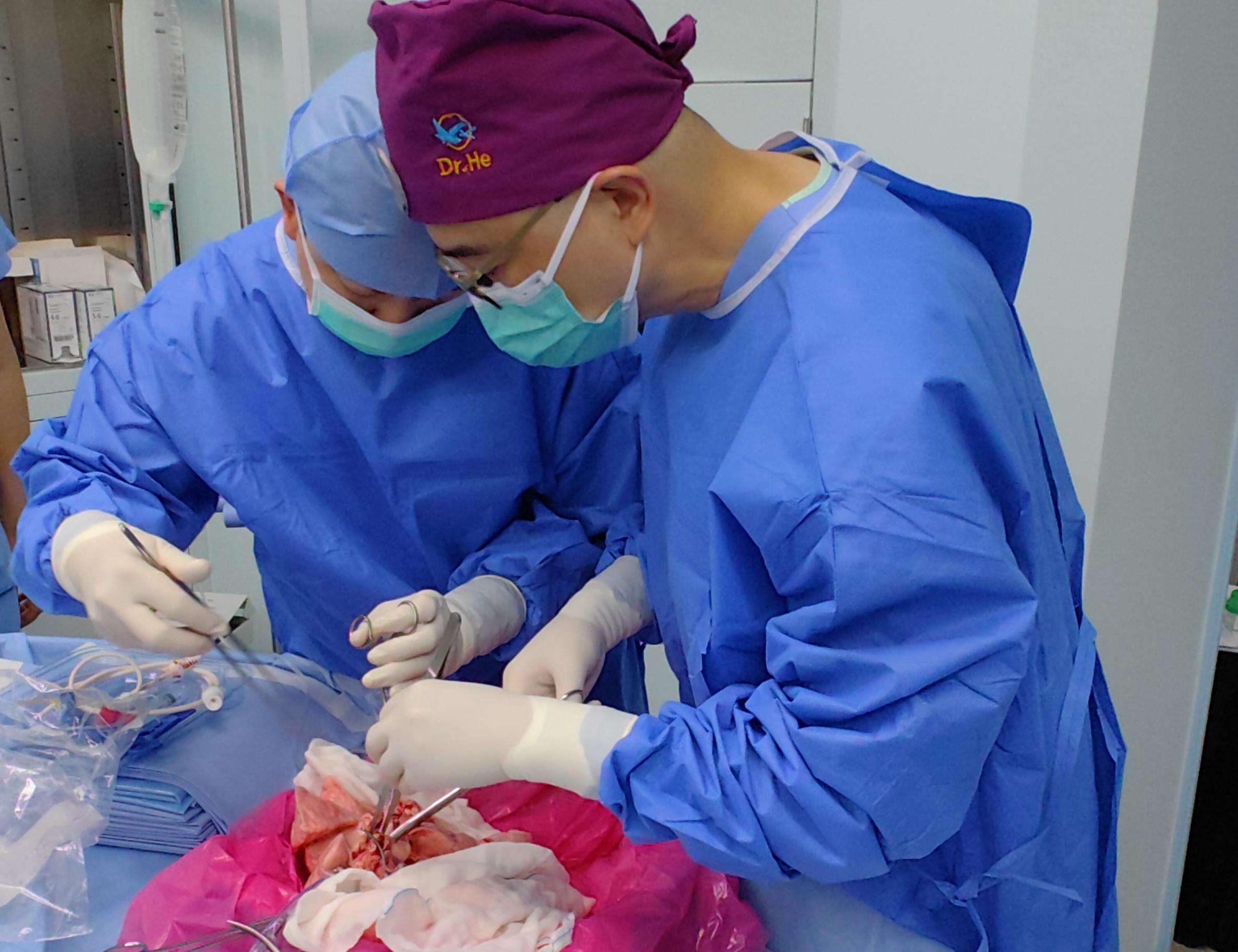
A modified pig liver was transplanted into a living person for the first time
A team from China has reported the results of the first liver transplant from a pig to a living human. Earlier this year, a procedure that served as a proof of concept was published, but it was performed on a brain-dead person. In this case, after modifying 10 genes in the porcine liver, an auxiliary transplant—not removing the entire organ—was performed on a 71-year-old patient with cirrhosis and liver cancer. It worked well for the first month, but on day 38, the graft had to be removed due to the development of complications, and the patient died on day 171. According to the researchers, who published the case in the Journal of Hepatology, this is "a fundamental step that demonstrates both the promise and the obstacles that remain to be overcome".