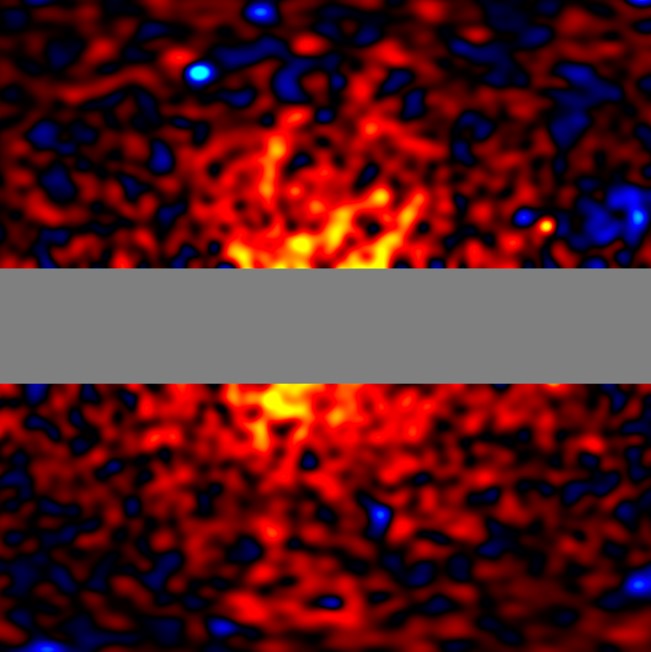
The Fermi space telescope detects gamma rays that could come from the decay of dark matter particles
A century ago, astronomer Fritz Zwicky observed that galaxies were moving faster than their mass should allow, leading him to infer the presence of an invisible structure, dark matter. Since the particles that make up dark matter do not interact with electromagnetic force, they cannot be observed directly, as they do not absorb, reflect, or emit light. Now, NASA's Fermi space telescope has found specific gamma rays in the center of the Milky Way that are consistent with the decay of theoretical dark matter particles, although they could also come from other sources. “If this is correct, to my knowledge, it would be the first time that humanity has ‘seen’ dark matter,” said study author Tomonori Totani in a press release. The article is published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.